ALK+ NSCLC is a distinct, targetable disease—often affecting younger, healthier patients who are frequently diagnosed in the later stages of the disease.5-7
NSCLC accounts for 80% to 85% of all lung cancer cases.8
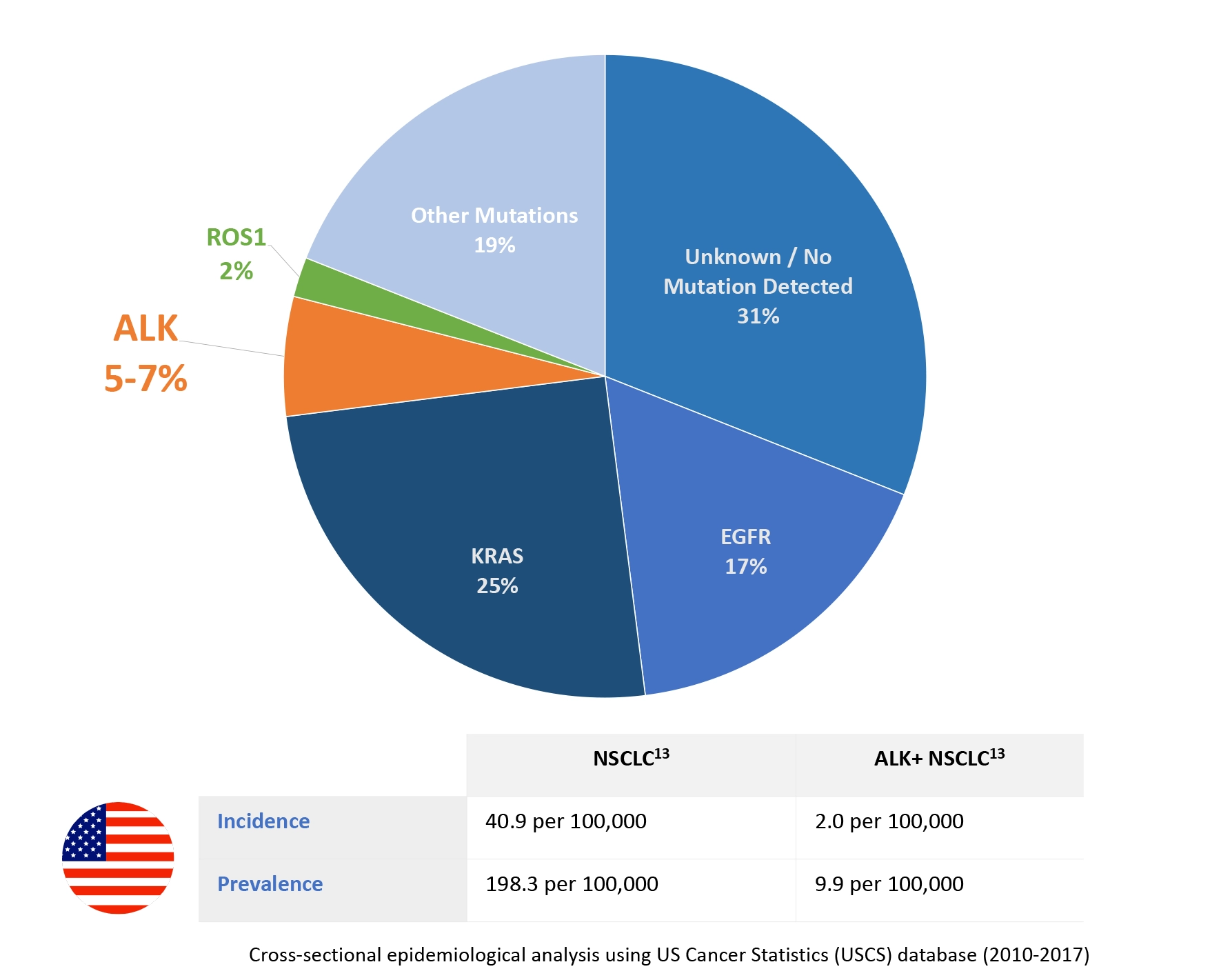
- 5% to 7% of cases are ALK+—a targetable driver mutation3,5,7,9
- ~10,000 new cases are diagnosed annually in the U.S.—reflecting an incidence of 2.89,10
Disease Overview

Younger patients—often diagnosed in the later stages of the disease6,11
Median age: ~52 (versus ~70 years for other types of NSCLC)6,11
- Significantly younger than the broader NSCLC population
- Often face a longer treatment journey

Non-smokers or light smokers6
~70% of patients with ALK+ NSCLC have never smoked12
Advanced disease at diagnosis11
~70% of patients are diagnosed with stage IIIb/IV11
- Late diagnosis limits opportunities for curative treatment11
Even with targeted treatment, long-term survival remains a challenge in ALK+ NSCLC.4
While incremental improvements have been achieved, survival is still low.4
- TKI inhibitors have offered promise in extending overall survival in ALK+ NSCLC4
- ALK+ NSCLC patients are currently treated with 1st, 2nd, and 3rd generation ALK inhibitors, yet 5-year survival is still only ~60%4
Unmet needs remain: Achieving consistent, long-term survival continues to be a significant area for improvement in the treatment of ALK+ NSCLC.4,14
CNS metastases are common, early, and progressive in ALK+ NSCLC.15,16
CNS metastases are associated with worse patient outcomes17
- ~70% of patients may develop CNS metastases18
- 8.5 months from diagnosis is the median onset of CNS metastases15,16